|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Meniere's disease
By Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Last updated on: March 11th, 2025 Meniere's disease causes balance and hearing problems. Learn more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and remedies for this inner ear disorder. Key points:
If you have sudden bouts of ear pressure, dizziness, hearing loss, and tinnitus, it could be Meniere's disease. The disease is named after Prosper Ménière, the French doctor who studied the disease in the 1800s. It primarily affects the hearing and balance organs, which are connected within the inner ear. What causes Meniere's?The cause is largely unknown. People with Meniere's disease most likely have a problem with too much pressure or fluid in their inner ear. However, doctors still don't know exactly why this happens. How common is Meniere's disease?According to the British Meniere's Society, the condition affects about 1 out of every 1,000 people. In about 10% of cases, there is a family history of the disease. It can affect people of any age, but it's most common in midlife. It usually only affects one ear.
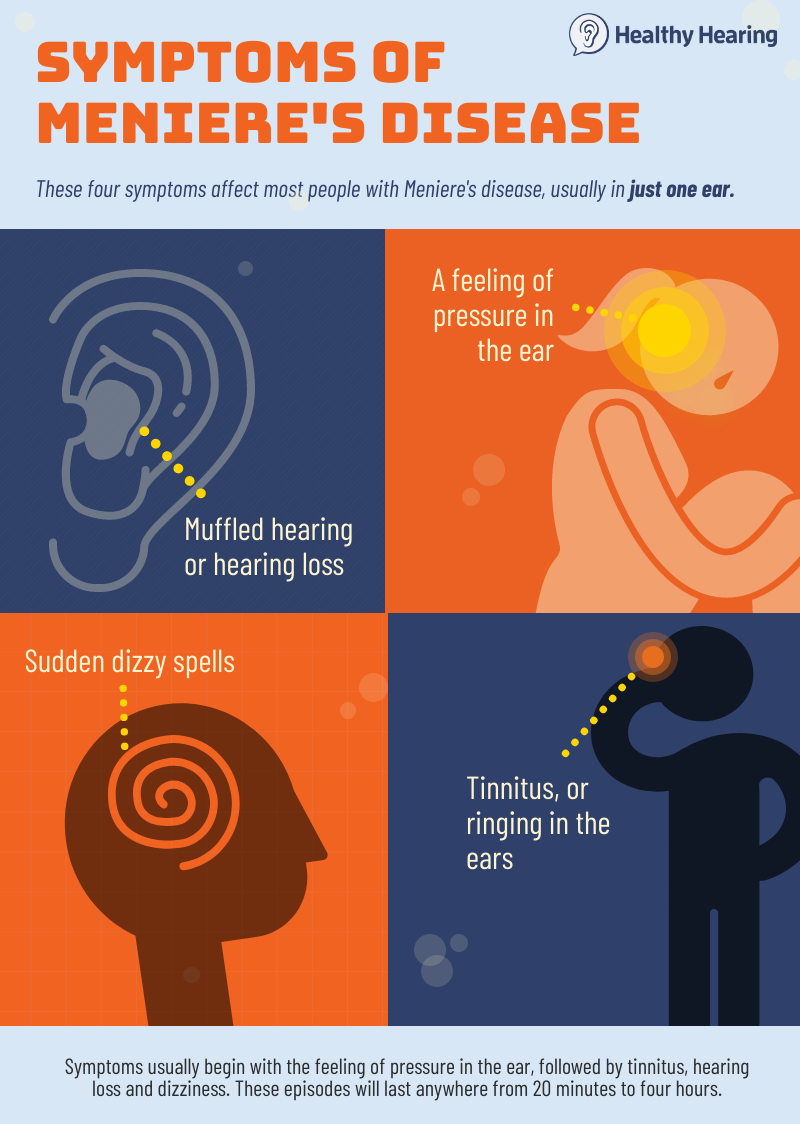
Key symptoms of Meniere's disease:
Other possible symptomsDuring an attack, a person's pupils may move rapidly from side to side, known as nystagmus. People with Meniere's disease also may struggle with "brain fog," or disoriented thinking and fatigue. Rarely, people also experience diplacusis, known as "double hearing." How often do Meniere's attacks occur?People will generally experience episodes in clusters with long periods of remission. Some sufferers will experience many attacks over a period of several days. Others will have an isolated attack. In other words, it's highly individual. How do I know if I'm about to have an attack?A Meniere's attack usually begins with the feeling of pressure in the ear, followed by tinnitus, hearing loss and vertigo. These episodes will last anywhere from 20 minutes to several hours. How do I make it go away?If you can, lie down and focus on one non-moving object, as this helps your inner ear rest. A nap may help, too. Any rescue medications you've been prescribed also may help, such as anti-nausea medication and anti-anxiety medication. Stages of Meniere's disease and diagnosis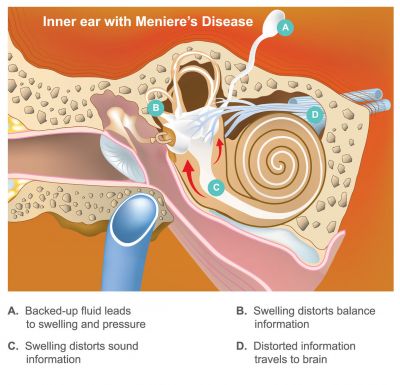
symptoms of Meniere's disease. Meniere's disease commonly affects people in various stages, with symptoms developing over time.
What is a drop attack?In rare cases, people with late-stage Meniere's disease may feel off balance and suddenly fall down but remain conscious and aware of what is happening. It can be very scary to experience a drop attack, and your doctor should be notified if you are experiencing them. In and of themselves they are not harmful, but they can lead to serious injuries. The website Dizziness and Balance has an in-depth page on drop attacks. Potential Meniere's triggersBasically anything that increases pressure or fluid in the inner ear can trigger an attack. However, triggers are different for everyone. Some of these may trigger a Meniere's episode in one person and not another:
How is Meniere's disease diagnosed?Repeated bouts of tinnitus, hearing loss and vertigo are strong indicators of Meniere's disease. Still, since all of these issues are common and can be associated with other diseases, Meniere's can sometimes be difficult to diagnose. "A full and accurate diagnosis may take many months to attain," write the authors of clinical practice guidelines published in the April 2020 issue of the Journal of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. Tests your doctor may orderThere is no single test to detect and diagnose Meniere's disease. Testing can help rule out other conditions, though. Tests may include:
Similar health conditionsMany health conditions can cause dizziness and other symptoms similar to Meniere's. These include autoimmune inner ear disease (a common cause of sudden hearing loss), otosclerosis, acoustic neuromas, acute labyrinthitis, temporal bone fracture, otosyphilis, vestibular neuritis, and vestibular migraines. These diseases generally respond to different treatment. If your only primary symptom is vertigo, it may be a common condition known as BPPV. Medical treatments for Meniere'sUnfortunately, many of the treatments for Meniere's haven't been studied extensively. The Cochrane Collaboration, which evaluates medical research, found only two treatments had any clinical trial evidence to support their use. Those are:
For either treatment, though, more study is needed to know how effective they are, researchers concluded. Other treatments for Meniere'sOther treatment options that have been less studied specifically for Meniere's include:
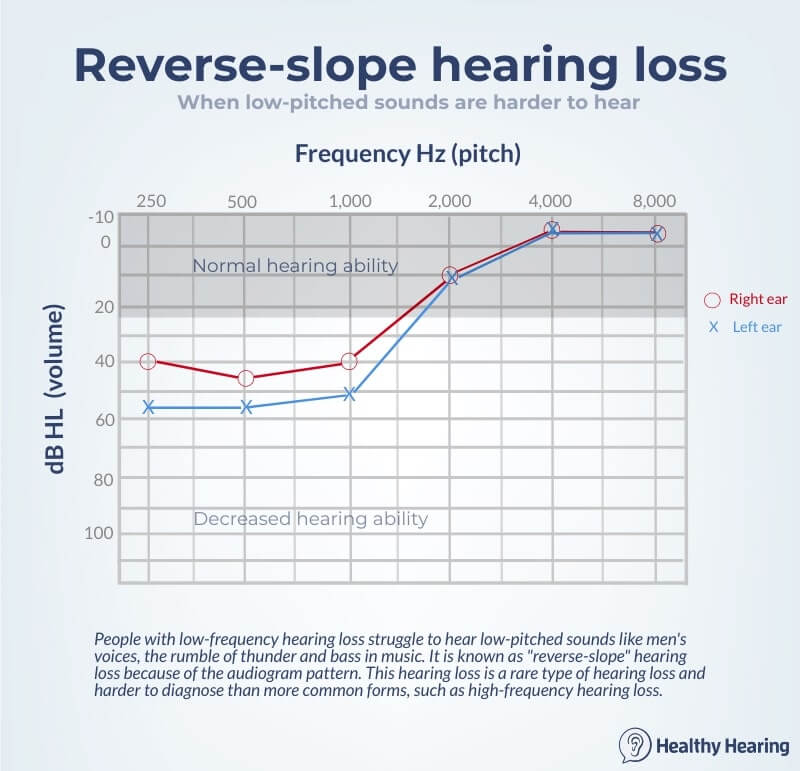
Hearing loss with Meniere's diseaseMeniere's disease can cause hearing loss in one or both ears. Often a person will struggle to hear low-frequency hearing loss, meaning low-pitched sounds may be harder to hear (men's voices compared to women's voices, or the bass in music, for example). It's also called "reverse-slope" hearing loss for the downward sloping pattern it makes on an audiogram.
However, Meniere's disease is unpredictable. The hearing loss may not affect low frequencies, but instead high frequencies. Often the hearing loss comes and goes, making it harder to diagnose. Some people will gradually develop more serious levels of hearing loss, which may be only in one ear or both ears. Hearing loss in one ear causes unique problems but can be treated. The hearing loss can range from mild to profound. A person also might be more sensitive to higher-pitched sounds and find them uncomfortable, known as hyperacusis. Treating hearing loss from Meniere'sHearing aids can generally help, since the type of hearing loss is sensorineural in origin. When hearing loss is severe, CROS hearing aids or cochlear implants may be recommended. Remedies and relief strategies for Meniere'sA variety of at-home remedies may help control Meniere's, although none of them have been studied extensively to know if they're effective or not. Meniere's diet recommendationsDietary changes may decrease the amount of fluid in the inner ear, which can weaken the symptoms of the disease. Researchers concluded there aren't any good clinical trials on diet and Meniere's disease. The good news? These changes are worth trying because they aren't harmful and may improve your overall health: 
symptoms of Meniere's disease.
More: How I manage Meniere's with a low-salt diet Other lifestyle changes that can help with Meniere's
Who treats Meniere's?Generally ear, nose and throat doctors, known as ENTs, or otolaryngologists, treat inner ear disorders. Neurologists and audiologists also may be on your healthcare team. If you experience symptoms of tinnitus, hearing loss and dizziness, see your primary care doctor for a referral to an ENT physician or visit a hearing center near you. Always seek help right away if you experience sudden hearing loss. Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing
You are reading about: Related topics More information about hearing loss, hearing aids, hearing aid brands and assistive devices. Featured clinics near me
Earzlink Hearing Care - Reynoldsburg Find a clinicWe have more hearing clinic reviews than any other site! Related contentThe Healthy Hearing Report |
|
www.HealthyHearing.com |
Meniere's disease
By Joy Victory, managing editor, Healthy Hearing  Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Reviewed by
Megan Gerhart, audiologist Last updated on: March 11th, 2025 Meniere's disease causes balance and hearing problems. Learn more about symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and remedies for this inner ear disorder. |


 Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.
Joy Victory has extensive experience editing consumer health information. Her training in particular has focused on how to best communicate evidence-based medical guidelines and clinical trial results to the public. She strives to make health content accurate, accessible and engaging to the public.